Circular Linked Lists
We have seen a Singular Linked List, a Double Linked List, now it's time to witness the Legen- wait for it- dary Circular Linked List. Which is basically a simple Linked list, the only difference being that the last node's Next pointer points to the head value of the Linked List.
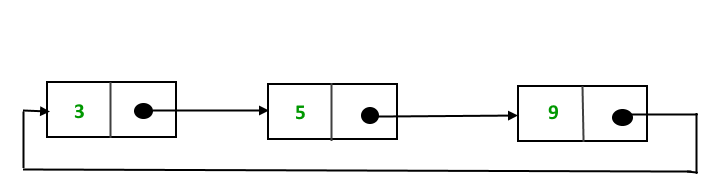
Let us see how insertion happens in a circular linked list.
We can add a node in 4 ways-
- Insertion in empty list
- Insertion at the beginning of the list
- Insertion at the end of the list
- Insertion in between the nodes
void addtoempty(Node *last, int data)
{
if(last!=NULL)
return last;
Node* temp= new Node(data);
last= temp;
temp->next=last;
return last;
}
Here we have linked this single node to itself.
Insertion at the beginning->
void addbegin(Node *last, int data)
{
Node* temp= new Node(data);
temp->next=last->next;
last->next= temp;
return last;
}
Here we have created a temp node, changed it's next pointer to that of last node's, later turned the next pointer of last to temp value.
Insertion at the end->
Very similar to how we insert at beginning, the only difference being is that we assign the new node value as the last node value
void addtoend(Node* last, int data)
{
Node* temp= new Node(data);
temp->next= last->next;
last->next=temp;
last=temp;
return last;
}
Insertion in between nodes->
We first need to search the right place to insert the node to maintain sorted property in a Linked list and then insert after.
void between(Node* last, int data, int item)
{
Node* temp, *p;
p=last->next;
//search the item
do{
if(p->data==item)
temp->data=data;
temp->next=p->next;
p->next=temp;
if(p==last)
last=temp;
return last;
}
p=p->next;
} while(p!=last->next);
return last;
}


